Structured Error Handler
Structured error format with context preservation and serialization for debugging, logging, and error transmission.
Overview
Structured Error Handler provides a rich error format that preserves context as errors propagate through call stacks. Unlike standard JavaScript errors that lose information when wrapped, this tool maintains the full history of operations, components, and metadata that led to a failure.
Status: Production Ready (v0.1.0)
Language: TypeScript
Repository: tuulbelt/structured-error-handler
Features
 Context Chain Preservation
Context Chain Preservation
Errors maintain a chain of context entries as they propagate up the call stack. Each layer can add its operation name, component, and metadata.
 Full JSON Serialization
Full JSON Serialization
Round-trip serialization to/from JSON for logging, transmission across network boundaries, and persistent storage.
 Error Codes & Categories
Error Codes & Categories
Assign error codes (like ENOENT, VALIDATION_FAILED) and categories (like io, validation, database) for programmatic error handling.
 Cause Chain Support
Cause Chain Support
Maintain the full cause chain from root error to top-level error. Navigate with getRootCause() and getCauseChain().
 Human-Readable Output
Human-Readable Output
Format errors for console output with context chain visualization and cause information.
 Zero Runtime Dependencies
Zero Runtime Dependencies
Uses only Node.js standard library. No external packages required at runtime.
Quick Start
# Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/tuulbelt/structured-error-handler.git
cd structured-error-handler
# Install dev dependencies
npm install
# Run examples
npx tsx examples/basic.ts
npx tsx examples/advanced.ts
# Run tests
npm testimport { StructuredError, serializeError } from './src/index.js';
// Create a structured error
const error = new StructuredError('Failed to process request', {
code: 'VALIDATION_FAILED',
category: 'validation',
operation: 'validateInput',
component: 'RequestHandler',
metadata: { field: 'email' }
});
// Check error type programmatically
if (error.hasCode('VALIDATION_FAILED')) {
// Return 400 Bad Request
}
// Serialize for logging
console.log(JSON.stringify(error.toJSON(), null, 2));Use Cases
 API Error Handling
API Error Handling
Wrap errors at each layer of your API with context, then serialize for logging and return appropriate HTTP responses.
 Database Error Chains
Database Error Chains
When a database query fails, wrap with context at repository, service, and controller layers while preserving the root cause.
 Structured Logging
Structured Logging
Serialize errors to JSON for structured logging systems. Includes full context chain and cause information.
 Error Routing
Error Routing
Use hasCode() and hasCategory() to route errors to appropriate handlers or return correct HTTP status codes.
Dogfooding
This tool demonstrates composability with other Tuulbelt tools:
Test Validation
Test Flakiness Detector - Validate test reliability:
./scripts/dogfood-flaky.sh 10
# Validates all tests are deterministicOutput Consistency
Output Diffing Utility - Verify serialization:
./scripts/dogfood-diff.sh
# Proves serialization produces identical outputSee DOGFOODING_STRATEGY.md for implementation details.
Demo
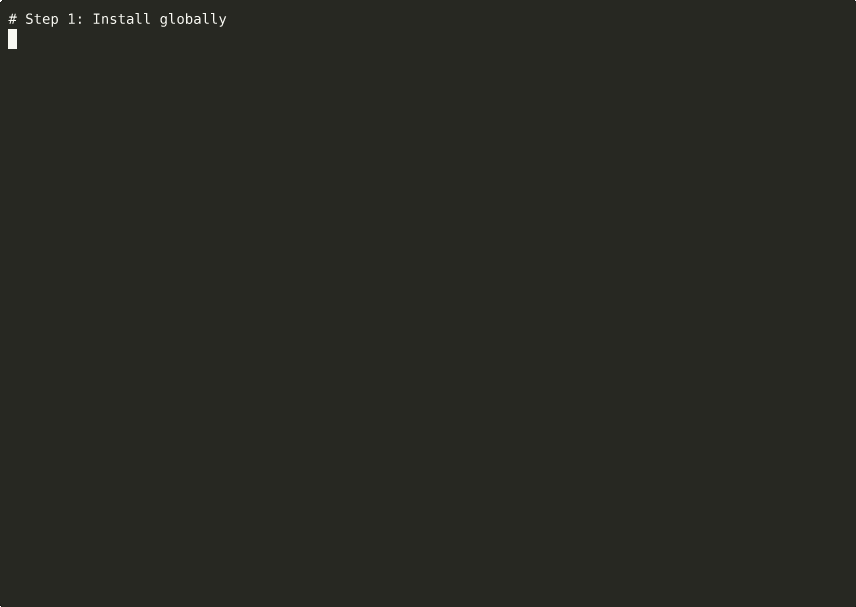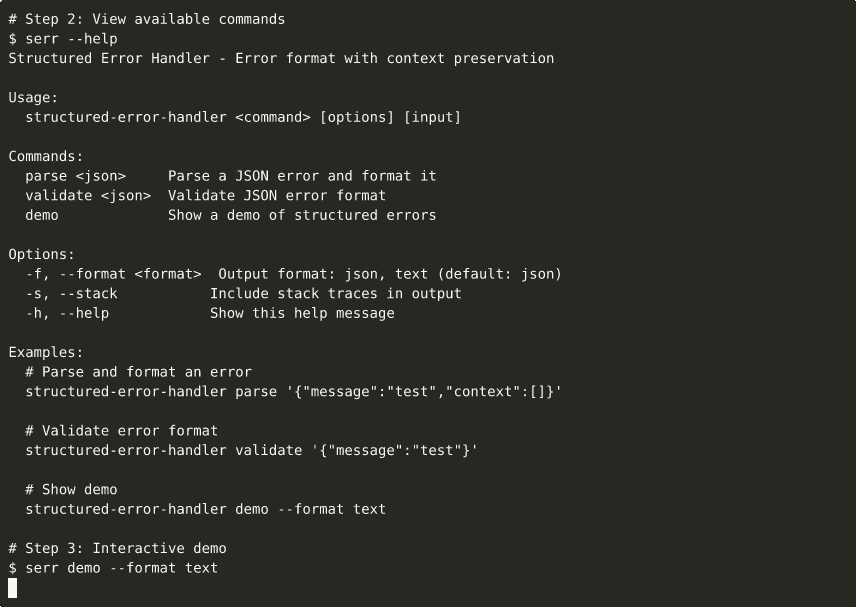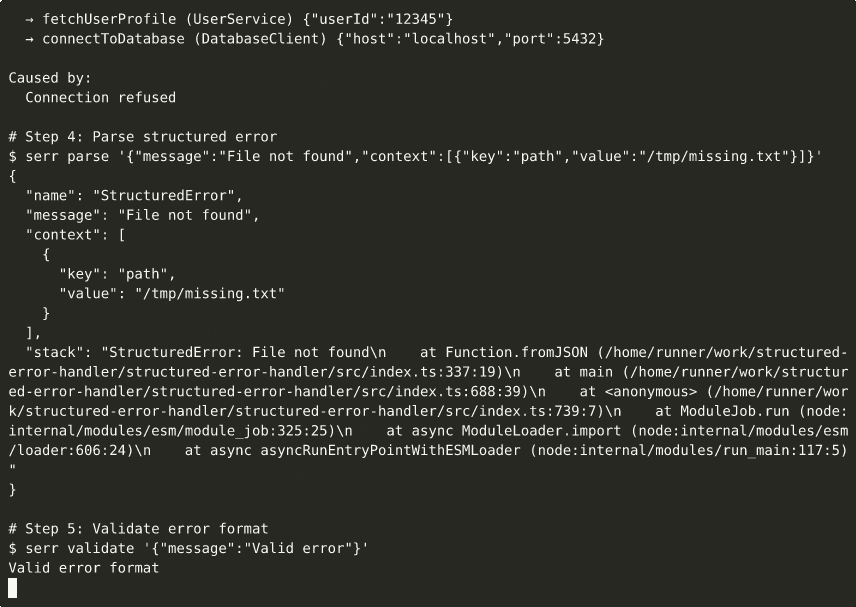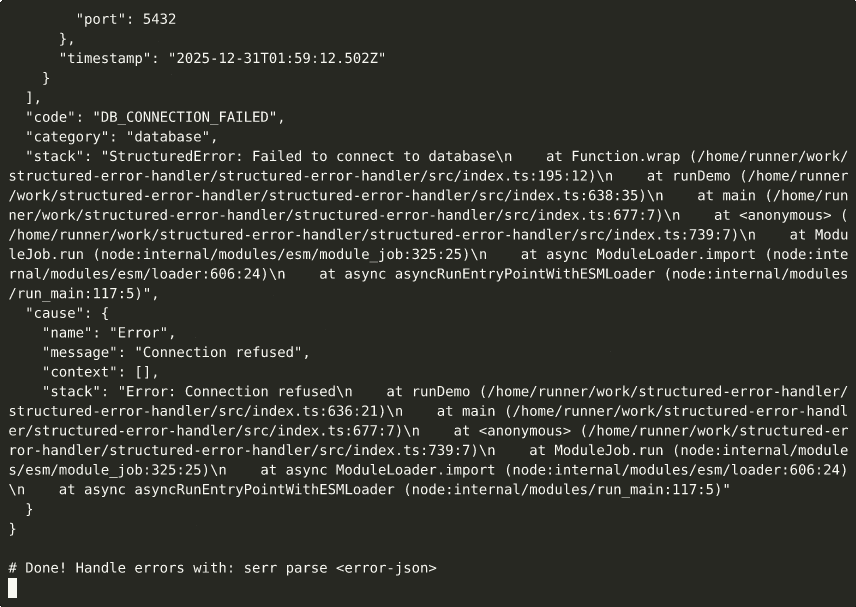
▶ View interactive recording on asciinema.org
Try it Locally
# Clone and setup
git clone https://github.com/tuulbelt/structured-error-handler.git
cd structured-error-handler
npm install
# Run CLI demo
serr demo
# Human-readable format
serr demo --format text
# Parse a JSON error
serr parse '{"message":"test","context":[]}'Demo recordings are automatically generated via GitHub Actions.
Context Chain Explained
Context is stored most recent first:
context[0] = handleRequest (most recent, top of call stack)
context[1] = fetchUser (earlier, one level down)
context[2] = queryDatabase (earliest, bottom of call stack)This matches the natural reading order when debugging: start from where the error surfaced.
Output Formats
JSON Format
{
"name": "StructuredError",
"message": "Failed to process request",
"code": "VALIDATION_FAILED",
"category": "validation",
"context": [
{
"operation": "handleRequest",
"component": "UserController",
"metadata": { "endpoint": "/api/users" },
"timestamp": "2025-12-26T12:00:00.000Z"
}
],
"cause": {
"name": "Error",
"message": "User not found",
"context": []
}
}Text Format
[VALIDATION_FAILED] Failed to process request
Context:
→ handleRequest (UserController) {"endpoint":"/api/users"}
Caused by:
User not foundWhy Structured Error Handler?
vs. Standard Error:
- Preserves context chain through re-throws
- Full JSON serialization support
- Error codes and categories for routing
vs. Error Cause (ES2022):
- Structured context at each level, not just message
- Metadata attached to each context entry
- Helper methods for cause chain navigation
vs. Custom Error Classes:
- Standardized format across your codebase
- Immutable enrichment pattern
- CLI tools for parsing and validation
Next Steps
- Getting Started - Installation and first error
- CLI Usage - CLI reference
- Library Usage - API examples
- Examples - Real-world use cases
- API Reference - Full API docs
Related Tools
- Test Flakiness Detector - Validates this tool's test suite
- Output Diffing Utility - Compare serialized errors
License
MIT License - See LICENSE
