Port Resolver
Concurrent port allocation for any application - avoid port conflicts in tests, servers, microservices, and development.
Overview
Port Resolver (portres) provides a centralized, file-based registry for port allocation. When running tests in parallel or multiple services in development, it ensures each process gets a unique port without conflicts.
Uses semats Library
This tool uses file-based-semaphore-ts as a library dependency for atomic registry access. See PRINCIPLES.md Exception 2 for details on Tuulbelt tool composition.
Status: Production Ready (v0.3.0) · 198 tests passing
Language: TypeScript
Repository: tuulbelt/port-resolver
Features
 File-Based Registry
File-Based Registry
Centralized port registry with atomic operations. Multiple processes coordinate without conflicts.
 Real Port Verification
Real Port Verification
TCP bind test confirms ports are actually available, not just recorded as free.
 Automatic Stale Cleanup
Automatic Stale Cleanup
Detects and removes stale entries from crashed processes based on PID checks.
 Semaphore-Protected
Semaphore-Protected
Uses file-based-semaphore-ts for atomic registry access.
 CLI & Library
CLI & Library
Use as a command-line tool for shell scripts or integrate as a TypeScript/JavaScript library.
 Zero Runtime Dependencies
Zero Runtime Dependencies
Uses only Node.js built-ins plus Tuulbelt tools (zero external dependencies maintained).
 Batch Allocation (v0.2.0)
Batch Allocation (v0.2.0)
Allocate multiple ports atomically with all-or-nothing semantics and per-port tag tracking.
 Port Lifecycle Management (v0.2.0)
Port Lifecycle Management (v0.2.0)
Track allocations by tag with PortManager for simplified port tracking and cleanup.
 Port Range Allocation (v0.2.0)
Port Range Allocation (v0.2.0)
Reserve contiguous port ranges for microservices clusters or get ports within specific bounds for firewall compliance.
 Tree-Shakable & Modular (v0.3.0)
Tree-Shakable & Modular (v0.3.0)
8 entry points for optimal tree-shaking. Import only what you need and save 40-80% bundle size.
Quick Start
# Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/tuulbelt/port-resolver.git
cd port-resolver
# Install dev dependencies
npm install
# CLI usage
portres get --tag "api-server"
# Output: 54321
# Release when done
portres release --port 54321// Library usage (v0.2.0 - PortManager)
import { PortManager } from '@tuulbelt/port-resolver';
const manager = new PortManager();
await manager.allocate('frontend');
await manager.allocate('backend');
await manager.allocate('database');
// Access by tag
const frontend = manager.get('frontend');
console.log(`Frontend port: ${frontend?.port}`);
// Release all at once
await manager.releaseAll();Demo
See the tool in action:
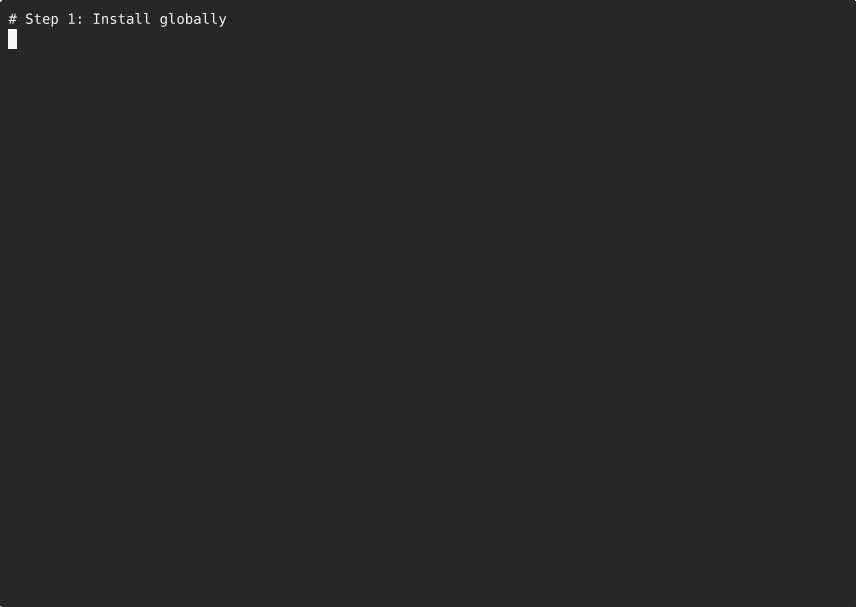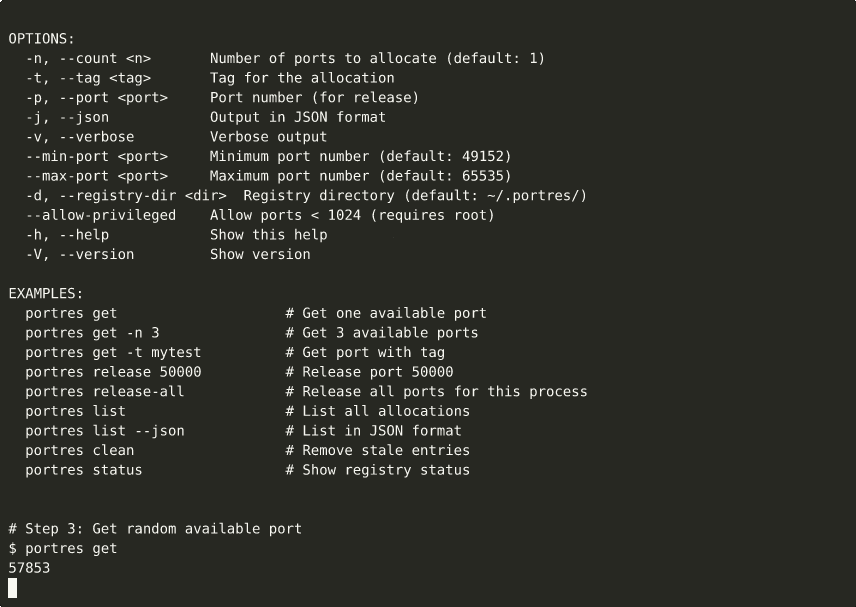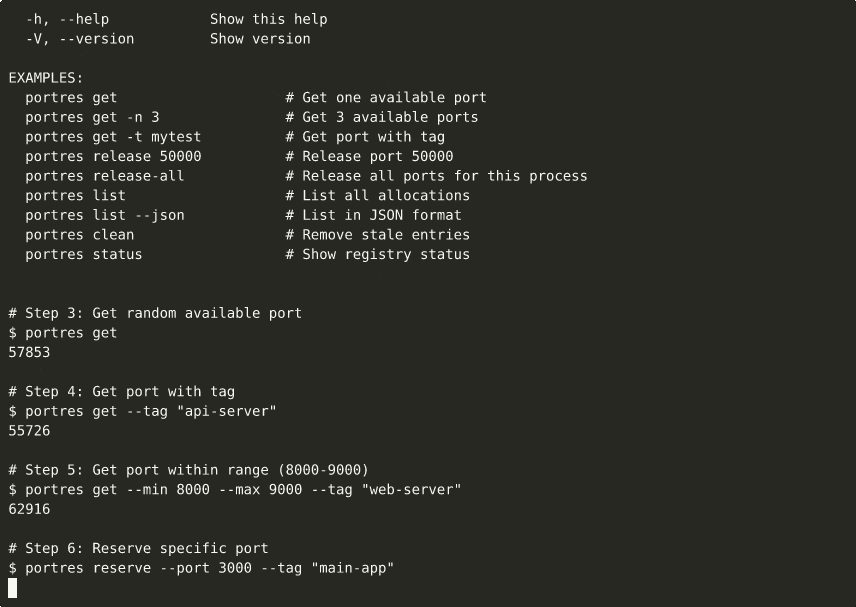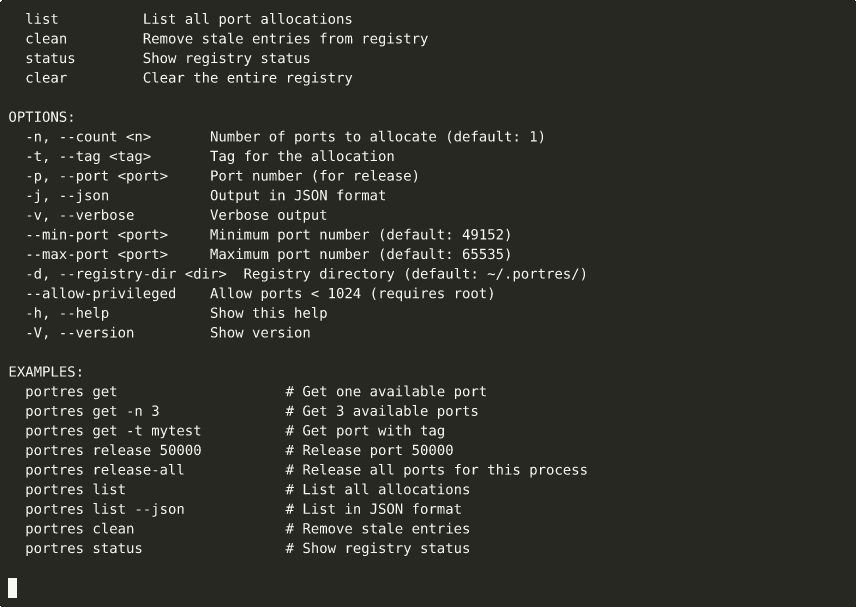
▶ View interactive recording on asciinema.org
Use Cases
- Parallel Test Workers: Running tests with
--workers=4or similar - Integration Tests: Tests that spawn servers or databases
- E2E Tests: Multiple services running simultaneously
- Development: Multiple microservices in local development
- CI/CD Pipelines: Avoiding port conflicts in shared runners
Why Port Resolver?
The common problem with hardcoded ports:
Error: listen EADDRINUSE: address already in use :::3000This happens because:
- Tests hardcode port numbers (
:3000,:8080) - Multiple test workers race for the same ports
- Flaky "works locally, fails in CI" behavior
Port Resolver solves this by providing a centralized registry with atomic operations.
API Overview
Module-Level (v0.2.0)
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
getPort(options?) | Convenience wrapper for single port allocation |
getPorts(count, options?) | Batch allocation with individual tags or shared tag |
PortManager Class (v0.2.0)
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
allocate(tag?) | Allocate port and track by tag (prevents duplicate tags) |
allocateMultiple(count, tag?) | Allocate multiple ports atomically |
release(tagOrPort) | Release by tag or port number (idempotent) |
releaseAll() | Release all managed ports |
getAllocations() | Get all tracked allocations |
get(tag) | Get specific allocation by tag |
PortResolver Class
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
get(config?) | Allocate a single port |
getMultiple(count, config?) | Allocate multiple ports |
reserveRange(options) | Reserve contiguous port range (v0.2.0) |
getPortInRange(options) | Get any port within specific bounds (v0.2.0) |
release(port) | Release an allocated port |
releaseAll(tag?) | Release all ports (optionally by tag) |
list() | List all allocated ports |
clean() | Remove stale entries |
status() | Get registry statistics |
Documentation
- Getting Started - Installation and setup
- CLI Usage - Command-line interface
- Library Usage - TypeScript/JavaScript API
- Examples - Real-world patterns
- API Reference - Full API documentation
Related Tools
- File-Based Semaphore (TS) - Atomic locking (used internally)
- Test Flakiness Detector - Detect unreliable tests
License
MIT License - see repository for details.
